How to Cultivate Emotional Intelligence in Teams
It was a warm afternoon when I found myself standing in line at the local grocery store. The queue was unusually long, and the woman ahead of me looked visibly frustrated. She sighed heavily, shifting her weight from one foot to the other and glancing repeatedly at her watch, as if that could somehow speed things up.
Meanwhile, the cashier at the counter, despite the steady stream of customers and complaints, remained calm and composed. She occasionally exchanged pleasantries with each shopper, her smile never wavering.
When it was finally the woman’s turn, she let out an exasperated sigh and started complaining about the long wait. The cashier, rather than responding defensively, met her gaze with understanding, empathized with her frustration, and assured her that they were doing their best to manage the rush. By the end of their brief exchange, the woman’s irritation seemed to dissolve, and she even managed a quiet apology as she left.
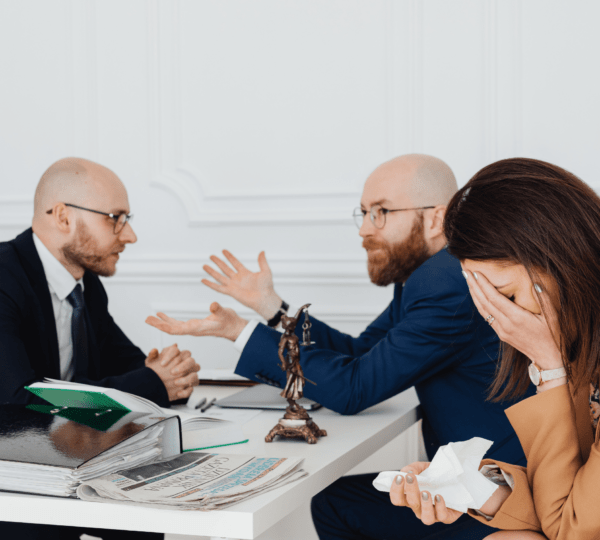
Reflecting on this encounter, I realized the cashier’s approach wasn’t just about good customer service; it was emotional intelligence (EI) in action. This skill isn’t just essential for defusing tense situations in a grocery store—it’s indispensable for fostering collaboration and trust in every aspect of life.
Cultivating emotional intelligence in teams isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s a must for building a resilient and productive workforce. Here’s how leaders and organizations can nurture this critical skill.
What Is Emotional Intelligence, and Why Does It Matter in Teams?
Emotional intelligence, often abbreviated as EI or EQ (emotional quotient), is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage your emotions while empathizing with others. Coined by psychologist Daniel Goleman, EI is broken into five key components:
- Self-awareness: Recognizing your emotions and how they affect your thoughts and actions.
- Self-regulation: Managing emotions in healthy ways, particularly in stressful situations.
- Motivation: Maintaining a positive outlook and intrinsic drive.
- Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others.
- Social skills: Building and maintaining healthy relationships.
In teams, EI fosters collaboration, reduces conflict, and enhances problem-solving. According to a 2022 study published in the Journal of Organizational Behavior, teams with higher collective EI outperform those with lower EI by up to 20% in tasks requiring cooperation and creativity.
Step 1: Start With Leadership
Cultivating emotional intelligence in teams begins with leadership. Leaders set the tone for team dynamics, and emotionally intelligent leaders inspire their teams to follow suit. According to Forbes, emotionally intelligent leaders:
- Model self-awareness by admitting mistakes and reflecting on their behavior.
- Exhibit empathy by actively listening to team members and validating their feelings.
- Promote a culture of psychological safety, where team members feel safe expressing their thoughts without fear of ridicule.
Practical Tips for Leaders:
- Conduct regular self-assessments using tools like the EQ-i 2.0 or Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT).
- Participate in EI training programs or coaching sessions to sharpen your skills.
- Share personal anecdotes of emotional growth to normalize vulnerability and foster trust.
Step 2: Foster Open Communication
Effective communication is the backbone of emotional intelligence in teams. Creating an environment where team members feel heard and understood can significantly boost morale and productivity.
How to Promote Open Communication:
- Active Listening: Encourage team members to listen without interrupting and summarize what they’ve heard before responding. According to Harvard Business Review, active listening improves team trust by 40%.
- Non-verbal Cues: Teach team members to be mindful of body language, tone, and facial expressions, which convey up to 93% of emotional meaning.
- Feedback Culture: Implement structured feedback systems, such as weekly check-ins or anonymous surveys, to ensure everyone’s voice is heard.
Step 3: Invest in Emotional Intelligence Training
Organizations can’t expect employees to master EI without proper training. Comprehensive workshops or online courses can equip teams with practical tools for emotional management and empathy.
Suggested Training Modules:
- Self-awareness exercises: Journaling, mindfulness practices, and reflective prompts.
- Role-playing scenarios: Simulating real-world conflicts to practice empathetic responses.
- Team-building activities: Group exercises like trust falls or collaborative problem-solving tasks.
Programs like those offered by the Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence and Coursera’s EI courses are excellent starting points.
Step 4: Create Opportunities for Collaboration
Teams often develop stronger emotional intelligence through shared experiences. Working together on challenging projects or cross-functional initiatives encourages team members to navigate emotions and resolve conflicts collaboratively.
Examples of Collaborative Practices:
- Cross-departmental projects: Rotate team members through different departments to diversify perspectives.
- Shared accountability systems: Assign collective goals to foster mutual support.
- Celebrating wins together: Recognize both individual and team accomplishments to reinforce positive emotional connections.
Step 5: Regularly Assess and Adjust
Cultivating EI is an ongoing process. Regular evaluations can help leaders identify gaps and make necessary adjustments.
Tools for Measurement:
- Pulse surveys: Quick, anonymous surveys to gauge team dynamics and emotional well-being.
- 360-degree feedback: Collecting input from peers, subordinates, and supervisors to get a holistic view of emotional intelligence.
- Behavioral observations: Tracking changes in team interactions over time.
Benefits of Emotional Intelligence in Teams
- Enhanced Collaboration: Teams with high EI navigate conflicts effectively and work cohesively.
- Increased Resilience: Emotional intelligence fosters adaptability during challenging times.
- Higher Job Satisfaction: Employees feel valued and understood, leading to improved morale.
- Improved Performance: Research from TalentSmart shows that 90% of top performers possess high EI.
Conclusion: Make Emotional Intelligence a Priority
Just as the barista’s calm demeanor transformed a tense situation, cultivating emotional intelligence can transform team dynamics. By prioritizing EI in leadership, communication, training, and collaboration, organizations create environments where employees thrive—not just professionally but emotionally. Start today by implementing one of these strategies and watch your team’s emotional intelligence flourish.
References
- Goleman, D. (1995). Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ. Bantam Books.
- “Emotional Intelligence in Leadership.” Forbes. https://www.forbes.com
- “Active Listening: The Key to Stronger Communication.” Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org
- TalentSmart. “Emotional Intelligence Statistics.” https://www.talentsmart.com
- “The Science of Team Emotional Intelligence.” Journal of Organizational Behavior, 2022.
- Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence. https://ei.yale.edu












